Isotopes of Hydrogen
Hydrogen-1 (¹H), also called protium, the simplest and most common form of hydrogen:
Hydrogen and Its Isotopes
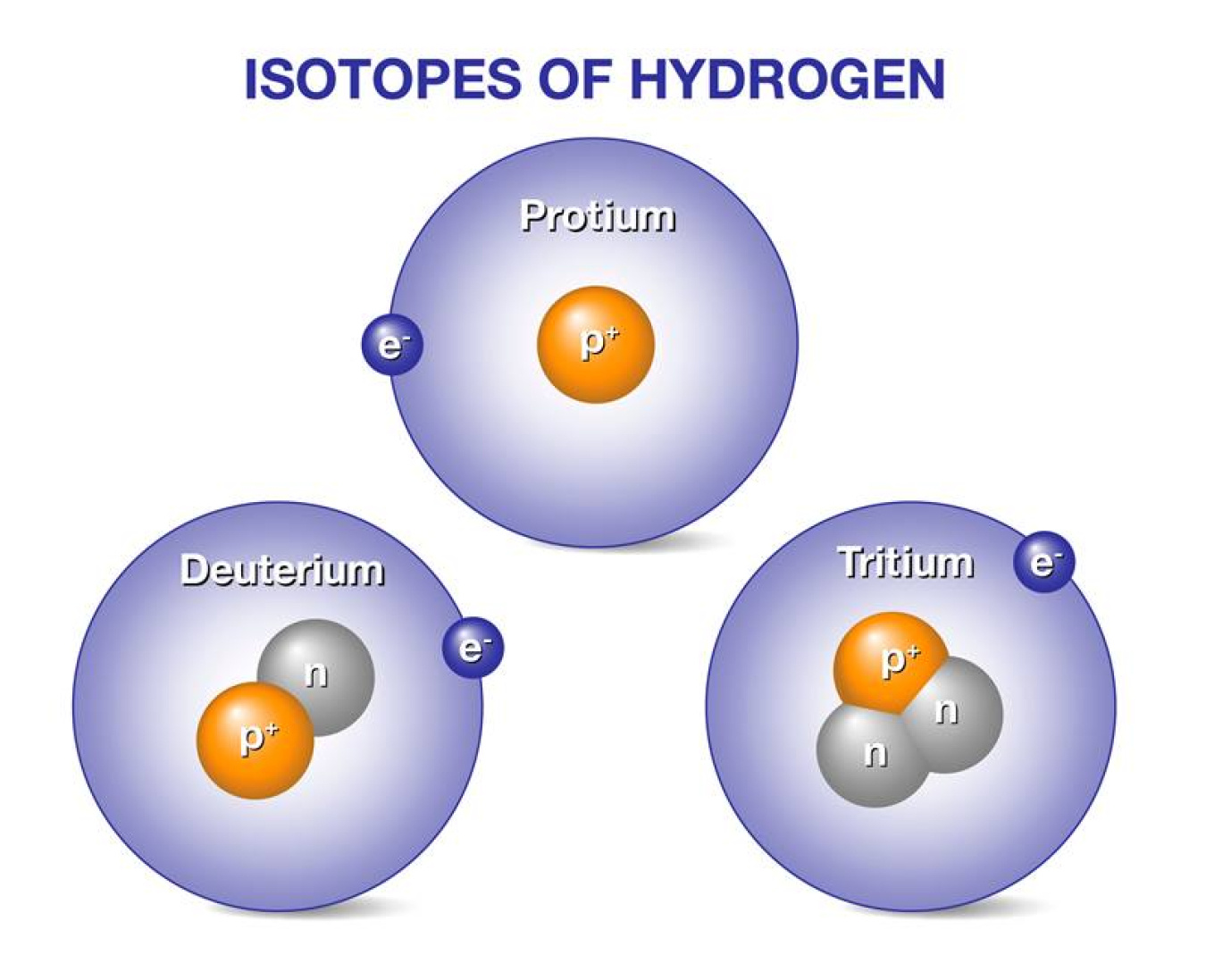
Hydrogen-1 (Protium)
| Property | Description |
| Name | Hydrogen-1 (Protium) |
| Symbol | ¹H or simply H |
| Atomic Number (Z) | 1 |
| Mass Number (A) | 1 |
| Isotopic Composition | 1 proton, 0 neutrons, 1 electron |
| Approximate Atomic Mass | 1.007825 u |
| Natural Abundance | ~99.985% of all hydrogen on Earth |
| Oxidation States | +1 (most common), −1 (in hydrides) |
| Group / Period | Group 1 (alkali metals) / Period 1 |
| Block | s-block |
| Element Category | Nonmetal |
2. Atomic and Subatomic Structure
Proton:Charge: +1 (1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹ C)
Mass: 1.007276 u
Electron:
Charge: −1 (−1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹ C)
Mass: 0.0005486 u
Neutrons:
None in protium (this is what distinguishes ¹H from deuterium or tritium).
Therefore, ¹H atom = 1 proton + 1 electron.
| Name | Symbol | Composition (protons / neutrons / electrons) | Approx. Atomic Mass (u or amu) | Notes |
| Protium (normal hydrogen) | H or ¹H 1 / 0 n / 1 e⁻ | 1.007825 u | Most abundant form (~99.985%) | |
| Deuterium D or ²H | 1 p / 1 n / 1 e⁻ | 2.014102 u | Heavy hydrogen isotope | |
| Tritium T or ³H | 1 p / 2 n / 1 e⁻ | 3.016049 u | Radioactive (half-life ≈ 12.32 years) |
Ion Masses (approximate)
When hydrogen (or its isotopes) lose or gain electrons, their mass changes slightly because an electron’s mass is small (~0.0005486 u).
| Ion | Composition | Approx. Mass (u) | Comment |
| H⁺ (proton) | 1 p / 0 n | 1.007276 u | Essentially just a proton |
| D⁺ (deuteron) | 1 p / 1 n | 2.013553 u | Nucleus of deuterium |
| T⁺ (triton) | 1 p / 2 n | 3.015501 u | Nucleus of tritium |
| H⁻ (hydride ion) | 1 p / 0 n / 2 e⁻ | 1.008 amu (approx.) | Extra electron adds tiny mass |
Do other Hydrogen Isotopes exist?
Yes
Hydrogen-4 (4H) - atomic mass 4.
Hydrogen-5 (5H) - atomic mass 5.
Hydrogen-6 (6H) - atomic mass 6.
Hydrogen-7 (7H) - atomic mass 7.
